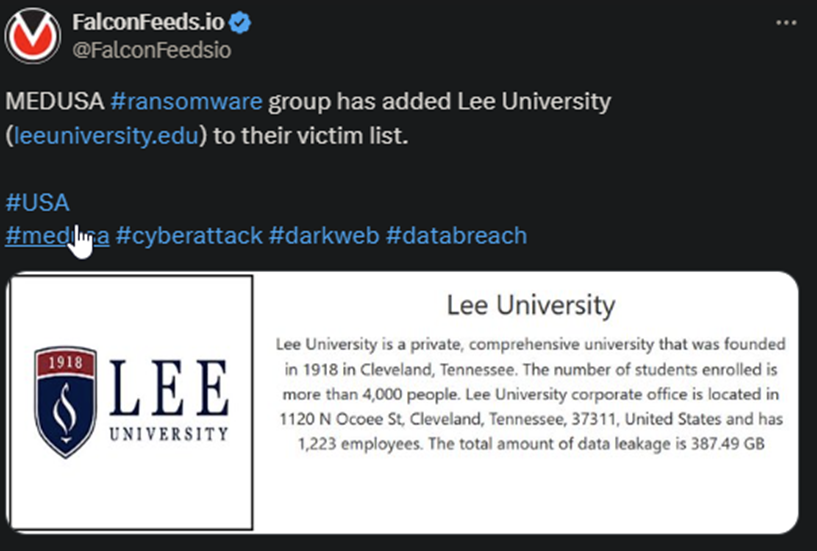
MEDUSA Hackers Breach US-Based Lee University
Lee University reportedly lost around 389 GB of confidential data as a result of the attack. It’s unclear what type of data was leaked or the ransom put forth by the hackers. The university houses up to 4,000 students and works with over 1,220 employees.
- MEDUSA has been more active recently compared to the previous year
- According to the latest statistics, the number of ransomware attacks is on an upward trend, and it’s unclear why that is
- The FBI, along with their foreign counterparts, have conducted several high-profile operations in an attempt to bring down specific actors
- MEDUSA operators posted the news about the breach on their public platform, along with a short summary of the institution
The MEDUSA gang has been active since 2021, but it started off slow and only gained popularity over time. Many confuse MEDUSA with MedusaLocker, which is a different, entirely unrelated organization.
Despite not ranking among the best and most successful ransomware entities in the world, MEDUSA can hold its own. The gang has been responsible for a series of attacks against high-profile targets.
One of these was the hit on Toyota Financial Services on 16 November 2023, during which the hackers demanded an $8 million ransom. Another was the Minneapolis School District hit, which resulted in a $100 million leak and $1 million ransom.
Finally, the gang’s most successful breach in terms of stolen assets was the September 2023 operation against Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PhilHealth.) The hackers demanded a ransom of $300,000, which the victim refused to pay.
Which wasn’t a total loss for MEDUSA, as the operators walked away with 750 GB worth of data.
How to Defend Your Company Against MEDUSA?
Prevention is the best policy, but that doesn’t say much on its own. The best course of action is to work with knowledgeable cybersecurity professionals to diagnose your system, detect vulnerabilities, and improve defenses.
Educating the staff is also critical to prevent breaches and identity threats in a timely manner. However, prevention alone isn’t enough. Cybercriminal gangs like MEDUSA are very proficient at what they do.
This means it’s unlikely that you will be able to put together a fail-proof defense system. So, at some point, you may be forced to accept the reality of being breached. What should you do then?
Most experts recommend the silent treatment. Don’t contact the hackers, don’t negotiate, and, more importantly, don’t pay anything. This will prevent you from ending up on the hackers’ “good payer” list, which opens you up to additional attacks over time.
It’s also important to learn that paying the ransom usually works against you. That’s because you have no way of verifying whether the hackers have actually deleted the data. In most cases, they don’t. They will provide you with the decryption key, but that’s it.
They will keep the leaked data for themselves and either use it or sell it to other cybercriminal gangs. And that’s the last thing you want.
Our Mission
We believe security online security matters and its our mission to make it a safer place.

